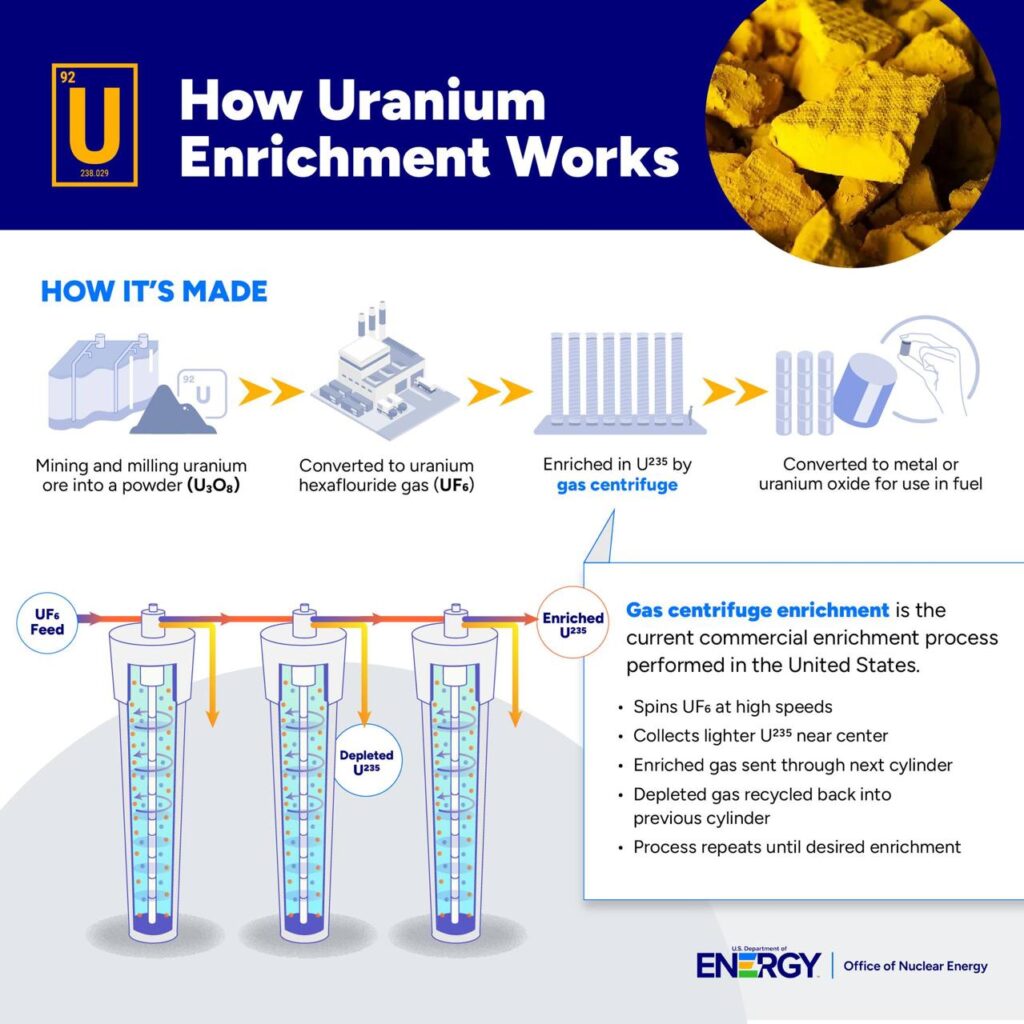
Centrifuge and Uranium Enrichment:
The process of uranium enrichment is crucial for both nuclear energy production and the development of nuclear weapons. A centrifuge is a key device used in this process to separate the fissile isotope uranium-235 (U-235) from natural uranium, which is mostly composed of the non-fissile isotope uranium-238 (U-238). This technology plays a significant role in energy security, international relations, and global security concerns.
—
## 1. Understanding Uranium Enrichment
### Composition of Natural Uranium:
– 99.3% Uranium-238 (**U-238**) – Not fissile but can be converted into Plutonium-239 in reactors.
– 0.7% Uranium-235 (**U-235**) – Fissile, meaning it can sustain a nuclear chain reaction.
### Requirement of Enrichment:
– Nuclear Power Reactors: Require uranium with 3-20% U-235, depending on the reactor design.
– Nuclear Weapons: Require uranium enriched to around 90% U-235.
Enrichment increases the proportion of U-235 in uranium fuel to make it usable for these applications.
—
## 2. Working of a Centrifuge
A centrifuge separates isotopes based on their slight difference in mass using centrifugal force.
### Process:
1. Conversion to Uranium Hexafluoride (UF₆):
– Since uranium is a solid metal in its natural state, it is first converted into uranium hexafluoride (UF₆) gas, which allows easier separation of isotopes.
2. Spinning in a Centrifuge:
– The UF₆ gas is fed into a high-speed centrifuge, which spins at around 50,000 revolutions per minute.
– The denser isotope (**U-238**) moves towards the outer edges.
– The lighter isotope (**U-235**) concentrates towards the centre.
3. Cascade Process:
– The slightly enriched U-235 sample is passed through multiple stages of centrifuges to gradually increase its concentration.
### Physics Behind Centrifugation:
The separation process follows the equation:
\[
F_c = m \times r \times \omega^2
\]
where:
– \(F_c\) = Centrifugal force
– \(m\) = Mass of the isotope
– \(r\) = Distance from the centre
– \(\omega\) = Angular velocity (rotation speed)
Since U-238 is slightly heavier than U-235, the force acting on it is greater, causing it to move outward while U-235 remains more central.
### Material Used in Centrifuges:
– The rotor of the centrifuge must withstand extreme speeds without breaking apart.
– Carbon fiber and other lightweight, high-strength materials are commonly used.
—
## 3. Global and Strategic Significance
### Energy Security:
– Countries with nuclear power programs require enriched uranium to fuel their reactors.
– Countries like India operate Pressurized Heavy Water Reactors (PHWRs) that use natural uranium, but Light Water Reactors (LWRs) require enriched uranium.
### Nuclear Non-Proliferation Concerns:
– The same technology used for peaceful nuclear energy can also be misused for making nuclear weapons.
– This has led to strict international monitoring by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA).
### Treaties and Agreements:
– Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT): Restricts uranium enrichment for weapons purposes.
– Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty (CTBT): Aims to prevent nuclear weapons testing.
– India’s 123 Agreement with the U.S.: Allows nuclear trade while adhering to non-proliferation norms.
—